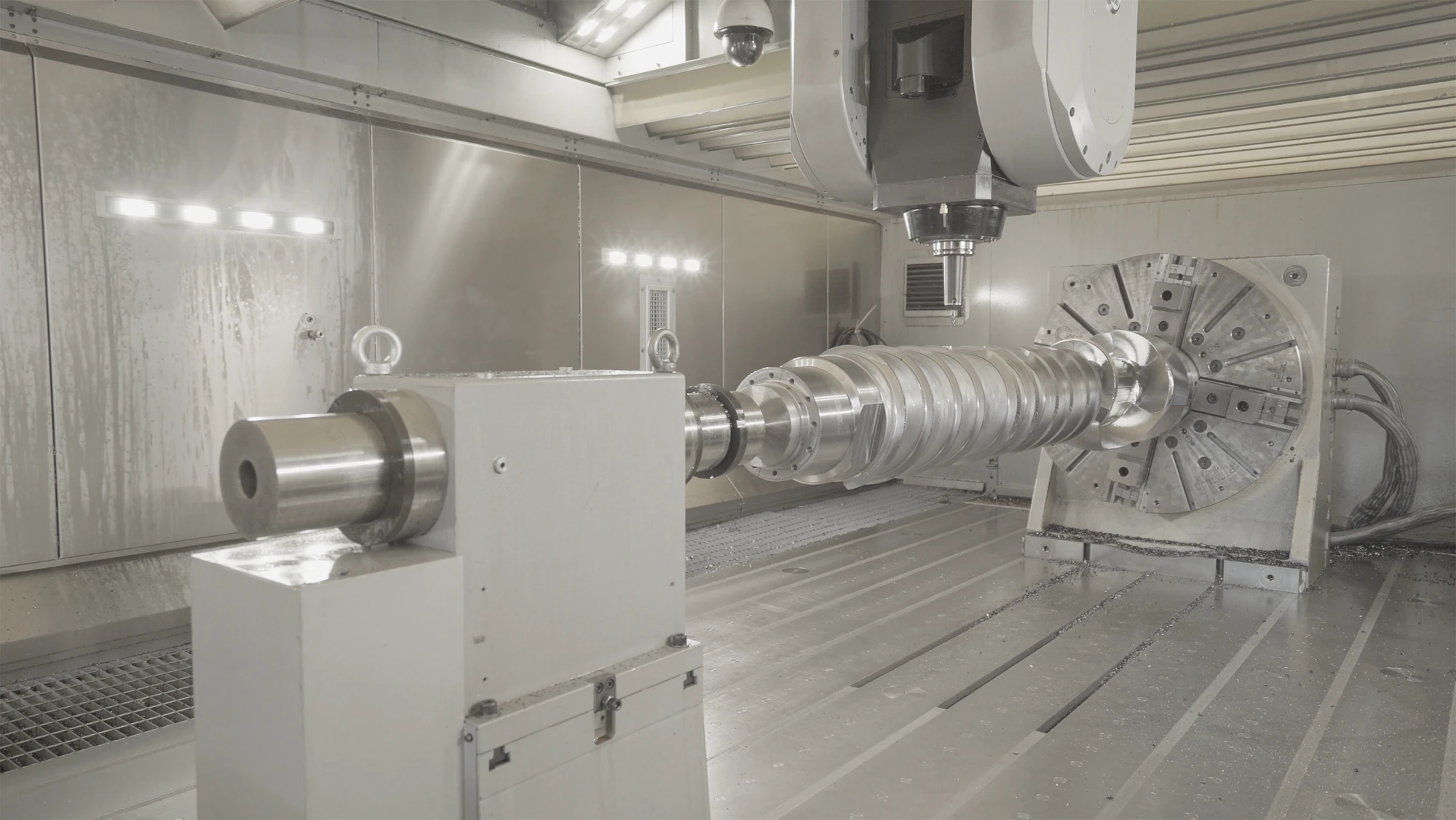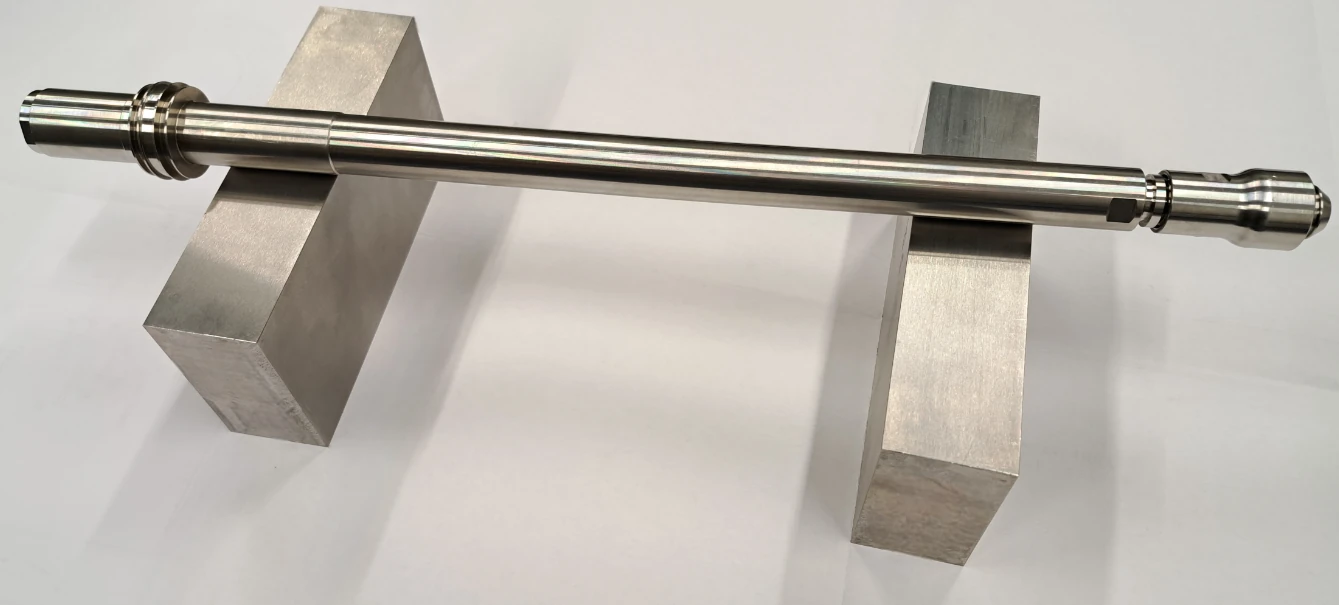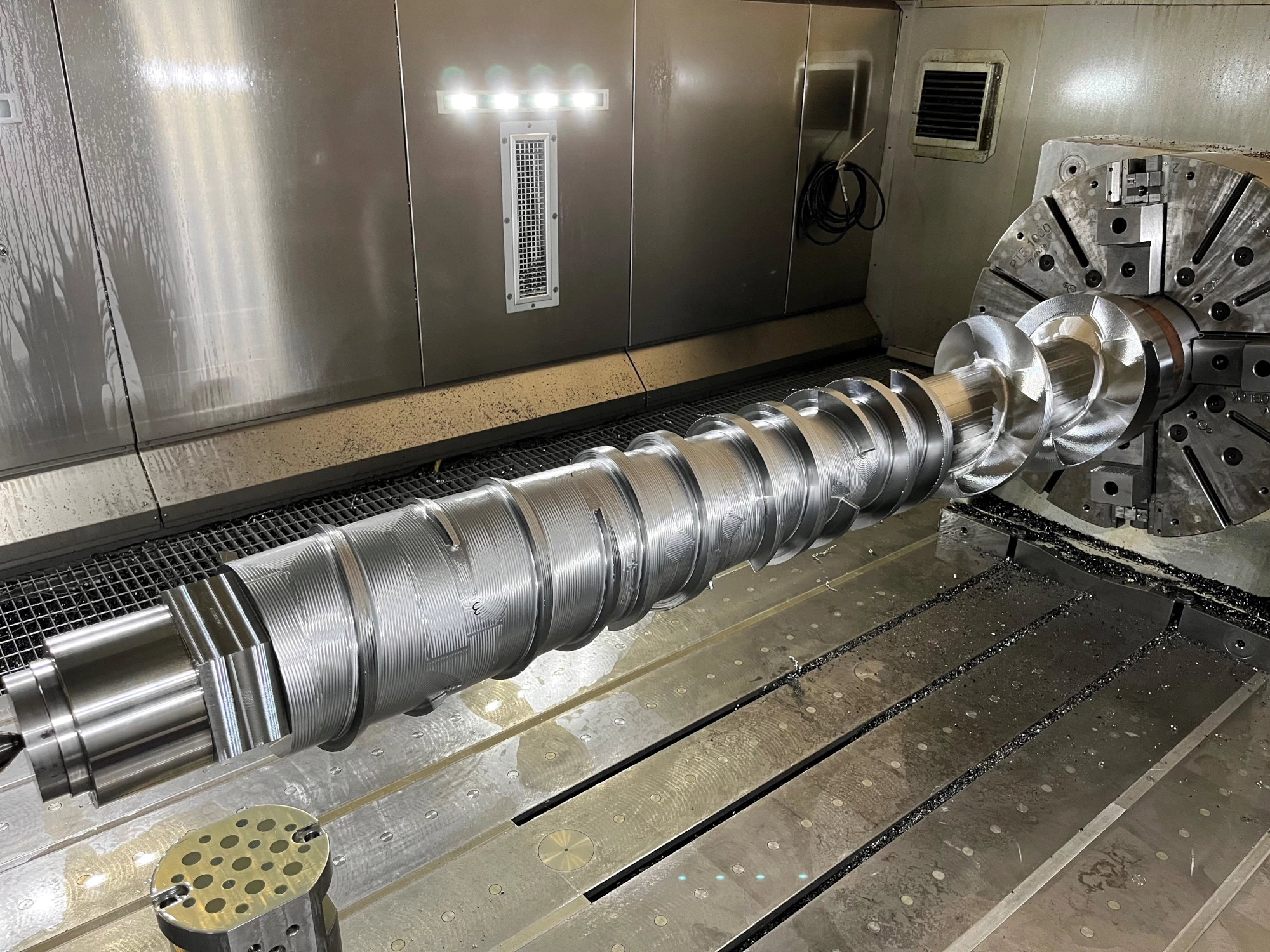
CNC TURNING
Turning is a precision machining process that uses a fixed cutting tool to remove material from a rotating workpiece (which can be metal, wood, or stone) to achieve the desired geometry. As the workpiece rotates, the cutting edge of the tool penetrates the surface, removing excess material (stock removal) and generating chips. This is why turning is one of the primary chip removal machining processes used in the metalworking industry.
The technical excellence of Steel Lavorazioni Meccaniche
With over 30 years of industry experience, Steel Lavorazioni Meccaniche stands out as a leader in precision machining, with specialized expertise in CNC turning.
Our multi-industry approach and ability to work with a wide range of materials allow us to meet the demands of highly specialized sectors, including aerospace, nuclear, and automation. Our certifications, aligned with the strict standards of the aerospace and nuclear industries, ensure fully traceable, controlled, and repeatable machining processes at every stage. We are committed to delivering reliability, superior quality, and on-time delivery for every project. These principles make us the ideal partner for companies seeking excellence in specialized precision machining.








WHAT IS CNC TURNING AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR?
CNC turning is an industrial machining process performed with a single-point cutting tool with a defined geometry, primarily used to create axisymmetric shapes.
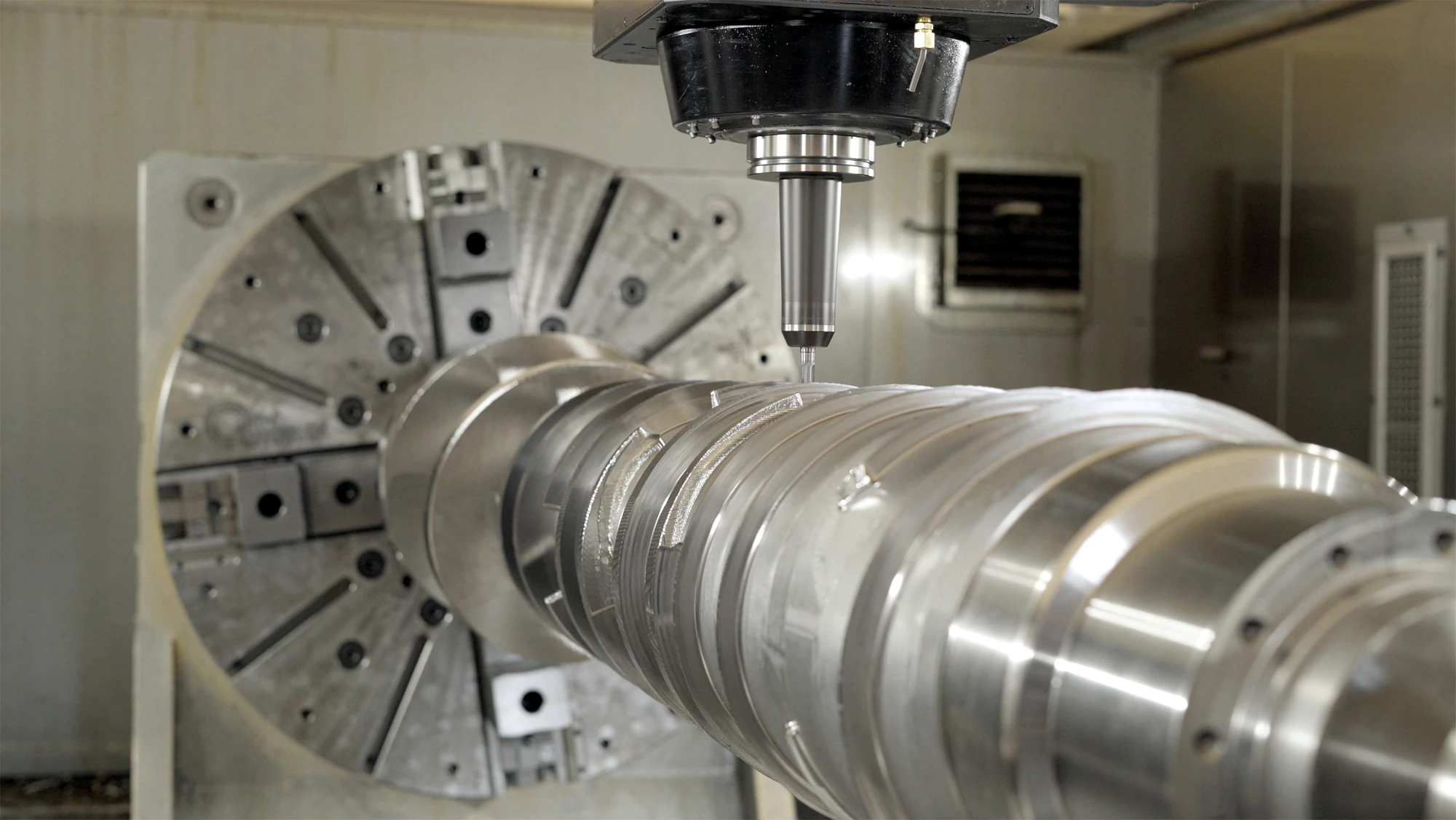
The process takes its name from the lathe, the machine tool required to perform turning operations. Although there are different types of lathes, they all operate on the same fundamental principle: removing a portion of material (chips) from a pre-defined workpiece to shape or profile it. Material removal is typically performed by a fixed cutting tool, controlled by an electronic system, while the workpiece rotates in different ways depending on the machining technique.
Below, we will explore the features of the lathe, the different types of CNC turning, and the main machining operations that can be performed with this process.
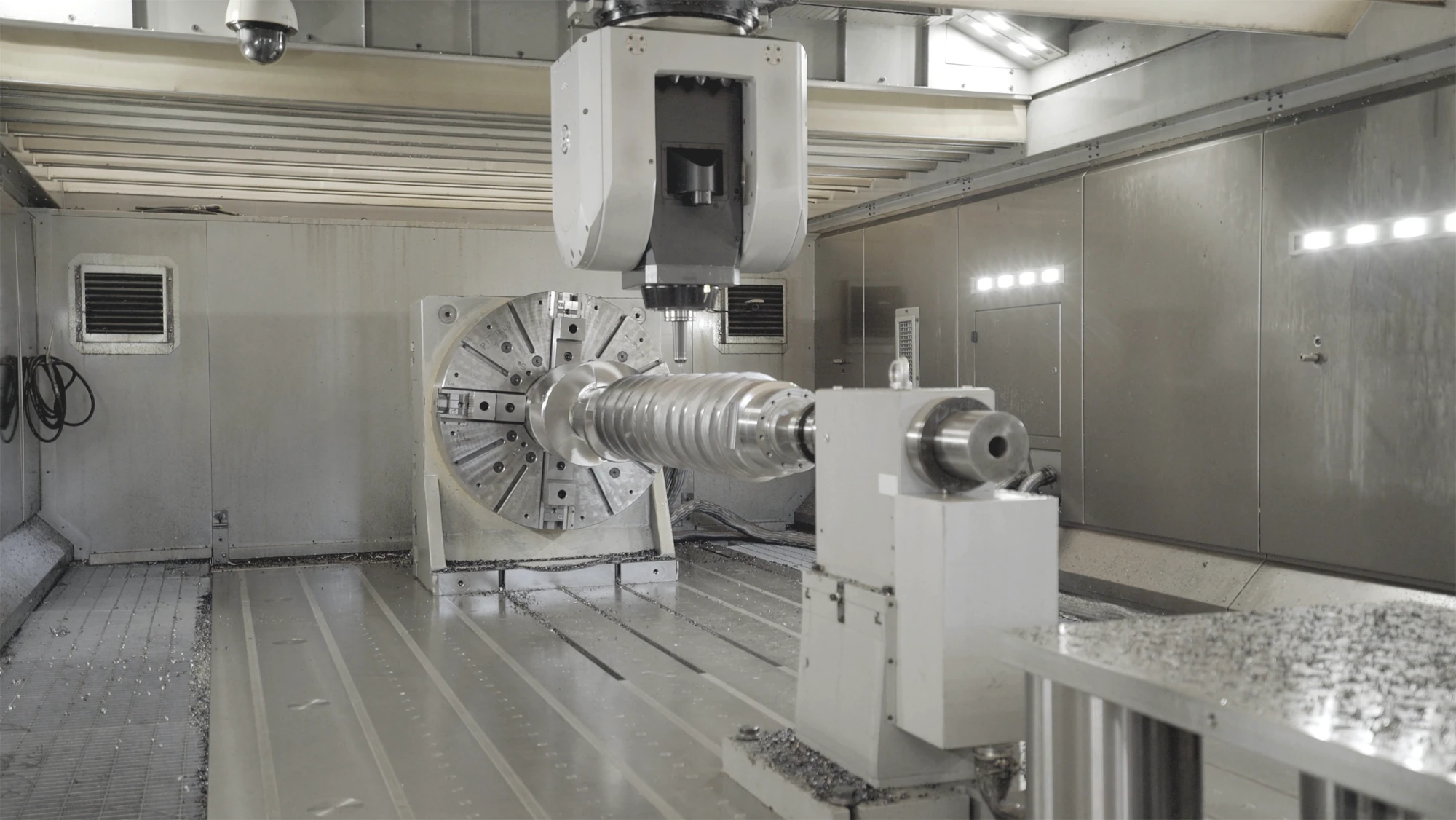
THE MACHINE TOOL FOR CNC TURNING: THE LATHE
The lathe is one of the oldest machine tools in history. In metalworking, various types of lathes are used, all sharing common features.
The workpiece is secured to a self-centering chuck, which rotates thanks to an electric motor. On the opposite side of the machine, the tool turret is mounted, allowing different turning tools, such as roughing, finishing, parting, and threading tools, to be used. In many cases, a tailstock support is present on the tool side, ensuring stability during machining.
For long and thin workpieces, which may bend or vibrate during machining and compromise accuracy, steady restsare used to support the workpiece, reducing deflection and vibrations.
Below are some of the most common types of lathes for metalworking:
DIFFERENT TYPES OF CNC TURNING BASED ON PARAMETERS
Turning is a highly versatile machining process that can be performed in various ways depending on the material being processed and the desired outcome.
Used for machining flat surfaces.
A process designed to create conical surfaces.
The machining operation that produces cylindrical shapes.
Used to create helical surfaces.
A specialized type of turning that enables the machining of complex surface geometries.
To achieve the desired turning operation, certain parameters must be adjusted based on the metal being machined, the tool material, and the tool size.
The distance the cutting tool moves relative to the workpiece per spindle revolution.
The speed at which the workpiece surface moves relative to the cutting edge of the tool during machining.
The rotational speed of the spindle, measured in revolutions per minute (rpm). It is calculated by dividing the cutting speed by the workpiece circumference. To maintain a constant cutting speed, spindle speed must be adjusted based on the cutting diameter.
The linear velocity of the tool relative to the workpiece, calculated by multiplying the cutting speed by the spindle speed.
The depth of the cutting tool along the axis of the workpiece during machining. Larger depths of cut require lower feed rates, or alternatively, the operation can be performed in multiple passes.
The depth of the cutting tool measured along the radius of the workpiece during turning. As with axial depth, larger radial depths require either multiple passes or a reduction in feed rate.
MAIN CNC TURNING OPERATIONS
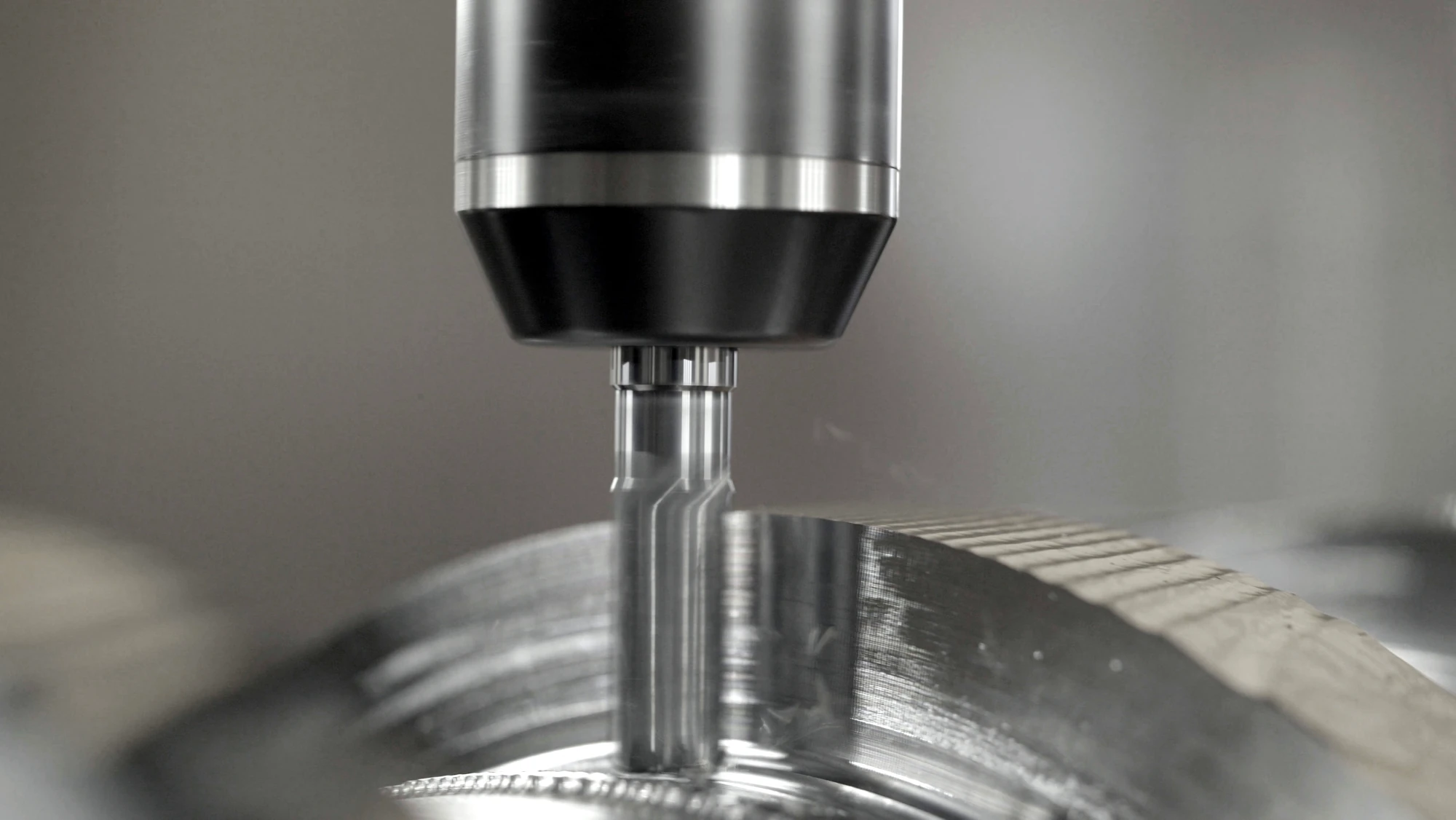
The turning process consists of two main phases: roughing and finishing. Roughing involves the removal of excess material, while finishing eliminates the remaining material to achieve the desired dimensions and surface roughness.
Turning operations can be classified as external or internal, depending on whether the tool machines the outer surface of the workpiece or performs an internal cut along the axis.
EXTERNAL OPERATIONS
A turning tool moves axially and radially along the workpiece axis, removing material to create features such as cones, chamfers, or steps. Typically, a small radial depth of cut is applied, and multiple passes are performed.
The tool moves radially along the end of the workpiece, removing a thin layer of material to produce a smooth and flat surface.
The tool moves radially into the workpiece, cutting grooves into its surface. Multiple passes may be used to create different groove geometries or to machine deeper grooves.
The cutting tool moves radially, similar to grooving, but continues to the center of the workpiece, separating a section.
A threading tool moves along the surface of the rotating workpiece, cutting the thread profile.
INTERNAL OPERATIONS
The drill bit penetrates the workpiece to create a hole. Unlike traditional drilling with a drill press, lathe drilling keeps the drill bit stationary, while the workpiece rotates.
Finishing operations used to refine holes. Unlike traditional boring and reamingperformed with drill presses or milling machines, lathe boring involves a rotating workpiece and a stationary cutting tool.
A tap tool enters the workpiece axially through a pre-drilled hole, cutting internal threads by removing material.
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MILLING AND TURNING?
Both milling and turning are essential chip removal machining processes and play a key role in precision mechanical manufacturing. However, they differ in operation and material processing methods.
In CNC turning, the workpiece rotates, while the cutting tool moves in a straight line. This allows the tool to shape and machine the material, achieving the desired form and dimensions.
In CNC milling, the cutting tool moves, while the workpiece remains fixed. The milling cutter is the tool that engages with the material. As it spins at high speed, it shapes and machines the workpiece.
The milling cutter can have various geometries, depending on the material being processed and the machining operation required.
WHY CHOOSE STEEL LAVORAZIONI MECCANICHE FOR CNC TURNING?
For over 30 years, Steel Lavorazioni Meccaniche has provided its customers with cutting-edge expertise and advanced technology to manufacture high-precision mechanical components through specialized machining processes.
The company offers a comprehensive service, built on extensive experience in CNC turning and precision machining.
Its diverse client portfolio has allowed the company to develop a multi-industry approach, gaining solid expertise in processing a wide variety of materials and building strong capabilities in producing high-performance components.
Steel Lavorazioni Meccaniche serves key industries such as aerospace, food processing, automation, packaging, recycling, and nuclear energy, ensuring:
The company is certified to meet the stringent standards required by the aerospace, military, and nuclear industries, guaranteeing top-tier quality and reliability.
All of this makes Steel Lavorazioni Meccaniche a leading company in the industry and the ideal partner for any industrial business in need of specialized CNC turning services,










